A fluid in which the velocity gradient is directly proportional to the shear stress. If two flat plates of area A are separated by a layer of fluid of thickness d and move relative to each other at a velocity v, then the rate of shear is v/d and the shear stress is F/A, where F is the force applied to each (see illustration). For a Newtonian fluid
F/A = µv/d
, where µ is the constant of proportionality and is called the Newtonian viscosity. Many liquids are Newtonian fluids over a wide range of temperatures and pressures. However, some are not; these are called non-Newtonian fluids . In such fluids there is a departure from the simple Newtonian relationships. For example, in some liquids the viscosity increases as the velocity gradient increases, i.e. the faster the liquid moves the more viscous it becomes. Such liquids are said to be dilatant and the phenomenon they exhibit is called dilatancy . It occurs in some pastes and suspensions. More common, however, is the opposite effect in which the viscosity depends not only on the velocity gradient but also on the time for which it has been applied. These liquids are said to exhibit thixotropy . The faster a thixotropic liquid moves the less viscous it becomes. This property is used in nondrip paints (which are more viscous on the brush than on the wall) and in lubricating oils (which become thinner when the parts they are lubricating start to move). Another example is the non-Newtonian flow of macromolecules in solution or in polymer melts. In this case the shearing force F is not parallel to the shear planes and the linear relationship does not apply. In general, the many types of non-Newtonian fluid are somewhat complicated and no theory has been developed to accommodate them fully. 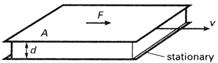
Newtonian fluid
- resonant cavity
- resonant circuit
- rest energy
- rest mass
- restitution coefficient
- resultant
- retardation
- retardation plate
- retina
- retrograde motion
- retrorocket
- reverberation time
- reverberatory furnace
- reverse osmosis
- reversible process
- Reynolds number
- rhe
- rheology
- rheopexy
- rheostat
- Richardson equation
- Richter scale
- rigidity modulus
- ring main
- ripple