The study of the interactions between a conducting fluid and a magnetic field. MHD is important in the study of controlled thermonuclear reactions in which the conducting fluid is a plasma confined by a magnetic field. Other important applications include the magnetohydrodynamic power generator (see illustration). In the open-cycle MHD generator a fossil fuel, burnt in oxygen or preheated compressed air, is seeded with an element of low ionization potential (such as potassium or caesium). This element is thermally ionized at the combustion temperature (usually over 2500 K) producing sufficient free electrons (e.g. K → K+ + e) to provide adequate electrical conductivity. The interaction between the moving conducting fluid and the strong applied magnetic field across it generates an e.m.f. on the Faraday principle, except that the solid conductor of the conventional generator is replaced by a fluid conductor. The power output per unit fluid volume (W) is given by
W = kσv2B2
, where σ is the conductivity of the fluid, v is its velocity, B is the magnetic flux density, and K is a constant. Devices of this kind are in use in some power stations, where they are suitable for helping to meet high short-term demands and have the ability of increasing the thermal efficiency of a steam-turbine generator from about 40% to 50%. In experimental closed-cycle systems the fluid is continuously recirculated through a compressor; the fluid consists of a heated and seeded noble gas or a liquid metal.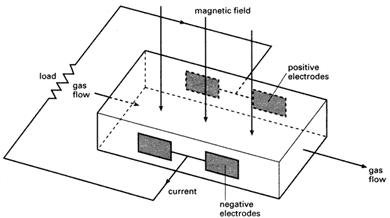
Magnetohydrodynamic generator
- phase speed
- phase transition
- phase-contrast microscope
- phases of the moon
- phasor
- phlogiston theory
- phon
- phonon
- phosphor bronze
- phosphorescence
- phot
- photino
- photocathode
- photocell
- photochemical reaction
- photochemistry
- photochromism
- photoconductive effect
- photodiode
- photodisintegration
- photoelasticity
- photoelectric cell
- photoelectric effect
- photoelectron
- photoelectron spectroscopy