An accumulator in which the electrodes are made of lead and the electrolyte consists of dilute sulphuric acid. The electrodes are usually cast from a lead alloy containing 7–12% of antimony (to give increased hardness and corrosion resistance) and a small amount of tin (for better casting properties). The electrodes are coated with a paste of lead(II) oxide (PbO) and finely divided lead; after insertion into the electrolyte a ‘forming’ current is passed through the cell to convert the PbO on the negative plate into a sponge of finely divided lead. On the positive plate the PbO is converted to lead(IV) oxide (PbO2). The equation for the overall reaction during discharge is:
PbO2+ 2H2SO4 + Pb → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
The reaction is reversed during charging. Each cell gives an e.m.f. of about 2 volts and in motor vehicles a 12-volt battery of six cells is usually used. The lead-acid battery produces 80–120 kJ per kilogram. Compare nickel-iron accumulator.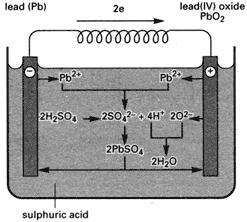
Lead-acid accumulator
- dilation
- dilatometer
- dimensional analysis
- dimensions
- diode
- dioptre
- dip
- dipole
- dipole radiation
- dipole-dipole interaction
- Dirac constant
- Dirac equation
- Dirac, Paul Adrien Maurice
- direct current
- direct motion
- direct-current motor
- directrix
- discharge
- discontinuous function
- disintegration
- disintegration constant
- diskette
- dislocation
- disordered solid
- disperse phase